Penile zipper injury
Disclaimer
These guidelines have been produced to guide clinical decision making for the medical, nursing and allied health staff of Perth Children’s Hospital. They are not strict protocols, and they do not replace the judgement of a senior clinician. Clinical common-sense should be applied at all times. These clinical guidelines should never be relied on as a substitute for proper assessment with respect to the particular circumstances of each case and the needs of each patient. Clinicians should also consider the local skill level available and their local area policies before following any guideline.
Read the full PCH Emergency Department disclaimer.
|
Aim
To guide PCH ED staff with the assessment and management of penile zipper injury.
Background
- A painful and anxiety-provoking complaint which can occur in the process of zipping or unzipping trousers.
- It is most commonly seen in pre-school and early school age boys.
- There has often been a pre-hospital attempt to free the entrapped tissues, which may have been distressing.
- As this is a relatively rare form of trauma, it is worth seeking the assistance of a colleague in the department who has had experience with a similar injury to enable help with management.
- It is important to be sensitive, especially with adolescents.
- It may be preferable to have male medical/nursing staff involved if possible.
There are two patterns of entrapment seen and the genital tissue may be:
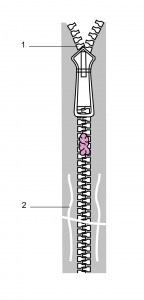 |
1. Entrapped in the mobile zipper head.
2. Caught between the interlocking teeth of the zipper.
|
Management
Preparation
- Keep the child in their most comfortable position (e.g. parents lap or supine on the bed).
- An explanation of the procedure along with reassurance and a gentle approach will help to gain a compliant patient.
Sedation and Pain management
- Analgesia is vitally important and should be given early. Consider intranasal fentanyl.
- Inhaled nitrous oxide sedation may be useful with aiding the removal procedure.
- Procedural sedation may be necessary for the distressed and anxious child.
Local Anaesthetic
- Topical local anaesthetic (e.g. lidocaine 2.5% with prilocaine 2.5% cream) applied for 45 - 60 minutes1 to numb the affected area.
Dorsal Penile Block
-
Some centres have advocated local infiltrate of lignocaine (never use adrenaline with this) but this is usually only required for significant skin or tissue entrapment (usually unnecessary).
- Mineral oil (lubricant) applied to the affected area for 10 minutes may assist to free the penile tissue when gentle traction is applied.
- It may be necessary to cut closely around the zipper so the rest of the trousers/jeans are no longer in the way. This must take place if the zip is to be cut through without causing any unnecessary traction on the exquisitely painful tissues.
Extraction manoeuvres
1. Entrapped in the mobile zipper head
Topical local anaesthetic (e.g. lidocaine 2.5% with prilocaine 2.5% cream) applied to affected area for 45 - 60 minutes1.
Gently attempt to pull the zip down. If unsuccessful:
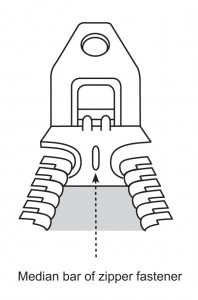 |
- Use wire cutters to cut through the median bar of the zipper fastener
- The front and back plates of the fastener will then fall apart and allow the zipper to be separated
|
2. Caught between the interlocking teeth of the zipper
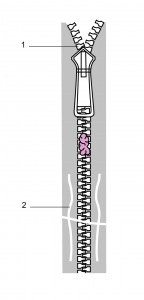 |
- If the skin is caught below the zip as shown in the diagram below, cut across the zip at point 2 (inferior to the entrapment site) to enable the two interlocking rows of the teeth to be gently pulled apart freeing the skin
|
If unsuccessful, referral to the Surgical team is warranted.
Post removal
- Ensure there has been no significant damage to the penile meatus.
- Other small lacerations or bruises usually heal very well.
- Significant injuries to the tissues should have surgical review.
Bibliography
- Australian Medicines Handbook Pty Ltd July 2021. Prilocaine; [Updated January 2025, Cited 25 July 2025]
- Bothner J (2014) Management of zipper injuries. UpToDate. Accessed at www.uptodate.com (external link)
| Endorsed by: |
Co-Director, Medical Services |
Date: |
Feb 2025 |
This document can be made available in alternative formats on request for a person with a disability.