Skin glue Dermabond
Disclaimer
These guidelines have been produced to guide clinical decision making for the medical, nursing and allied health staff of Perth Children’s Hospital. They are not strict protocols, and they do not replace the judgement of a senior clinician. Clinical common-sense should be applied at all times. These clinical guidelines should never be relied on as a substitute for proper assessment with respect to the particular circumstances of each case and the needs of each patient. Clinicians should also consider the local skill level available and their local area policies before following any guideline.
Read the full CAHS Clinical disclaimer
|
Aim
To guide PCH ED staff with the use of Dermabond® topical skin adhesive (skin glue).
Background1,2
Indications
- Simple clean superficial lacerations (less than 3 cm)
- Good wound approximation
- Low wound tension
Contraindications
- Jagged lacerations
- Bites, punctures or crush wounds
- Contaminated wounds
- Mucosal surface
- Axillae and perineum (high moisture areas)
- Hands, feet and joints (unless kept dry and immobilised)
Properties
- Maximum bonding strength is at 3 minutes
- Can be applied without anaesthetic
- Water resistant
- The glue will slough off within 5-10 days
- Equivalent cosmetic result to sutures
Procedure
Assistance with the procedure will generally be required, especially with an active child.
- Apply topical anaesthetic (Laceraine®) if required to stop the bleeding
- Wait 30 minutes if Laceraine is applied
- Irrigate with sodium chloride 0.9%
- Dry with sterile gauze
- Appose wound edges
- Crush Dermabond® vial and invert
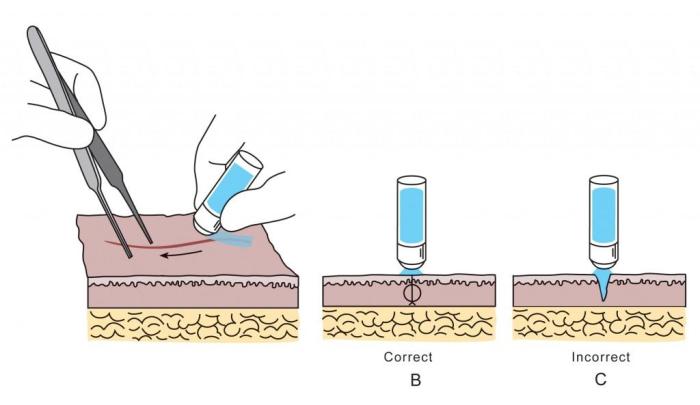
- Gently brush adhesive over laceration
- Do not place glue into the wound - this will impair wound healing and lead to wound dehiscence
- Wait 30 seconds
- Apply second layer in an oval motion around the wound – coverage of a larger skin surface area adds to strength of wound closure
- Apply a third layer after a further 30 seconds if required
- No dressing is required but in young children a dressing may be applied to prevent picking of the glue
Lacerations near the eye
Care should be taken when using skin glue near the eye.
Methods to prevent glue entering the eye:
- Lower the head end of the bed
- Apply Vaseline between the wound and the eye
- Hold gauze over the eye
- Ensure the child is compliant or well held
- In the unfortunate event of glue getting in the eye, wash immediately with water and use Vaseline to soften the glue
Bibliography
- Bruns, T B, and J M Worthington. "Using Tissue Adhesive for Wound Repair: A Practical Guide to Dermabond." American Family Physician 61.5 (2000): 1383. Web. Available from: Using Tissue Adhesive for Wound Repair: A Practical Guide to Dermabond. - American Family Physician (aafp.org)
- Lin, Michelle, Wendy C Coates, and Roger J Lewis. "Tissue Adhesive Skills Study: The Physician Learning Curve." Pediatric Emergency Care 20.4 (2004): 219-23. Web. Available from: Tissue Adhesive Skills Study: The Physician Learning Curve (health.wa.gov.au)
| Endorsed by: |
Nurse, Co-director, Surgical Services |
Date: |
Feb 2023 |
This document can be made available in alternative formats on request for a person with a disability.